|
Intel 850
The Intel 850 chipset was the first chipset available for the Pentium 4 processor, and was simultaneously released in November 2000. It consists of an 82850 memory controller hub and an 82801BA I/O controller hub. This chipset outperforms the AMD 760 chipset with the 266 MHz FSB. Despite using (supposedly) high-performance expensive RDRAM, performance was mediocre at best. In early 2002, this chipset was superseded by the Intel 845, which used slower but much less expensive SDRAM or DDR SDRAM. The Intel 855 chipset released at the same time as the Pentium M and Celeron M, and the lower Intel 852 chipset are completely different products and are not covered in this article. Features *Socket 423 or Socket 478 CPU compatible with 400 MHz FSB *Supports P4 CPUs at 1.3 GHz or Faster *Four PC800 RDRAM slots compatible with ECC *Up to 2 GB memory supported. *AGP 4X slot Intel 850E The Intel 850E chipset added PC1066 RDRAM support and 533 MHz FSB support. Overv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 850E MCH
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce (1927–1990) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. The production of Netburst processors was active from 2000 until May 21, 2010. All Pentium 4 CPUs are based on the NetBurst microarchitecture. The Pentium 4 '' Willamette'' (180 nm) introduced SSE2, while the '' Prescott'' (90 nm) introduced SSE3. Later versions introduced Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT). The first Pentium 4-branded processor to implement 64-bit was the ''Prescott'' (90 nm) (February 2004), but this feature was not enabled. Intel subsequently began selling 64-bit Pentium 4s using the ''"E0" revision'' of the Prescotts, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel's name for the NX bit) to Intel 64. Intel's official launch of Intel 64 (under the name EM64T at that time) in mainstream deskt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Controller Hub
In computing, a northbridge (also host bridge, or memory controller hub) is one of two chips comprising the core logic chipset architecture on a PC motherboard. A northbridge is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB) to handle high-performance tasks, and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. Since the 2010s, die shrink and improved transistor density have allowed for increasing chipset integration, and the functions performed by northbridges are now often incorporated into other components (like southbridges or CPUs themselves). As of 2019, Intel and AMD had both released chipsets in which all northbridge functions had been integrated into the CPU. Modern Intel Core processors have the northbridge integrated on the CPU die, where it is known as the uncore or system agent. On older Intel based PCs, the northbridge was also named external memory controller hub (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I/O Controller Hub
I/O Controller Hub (ICH) is a family of Intel southbridge microchips used to manage data communications between a CPU and a motherboard, specifically Intel chipsets based on the Intel Hub Architecture. It is designed to be paired with a second support chip known as a northbridge. As with any other southbridge, the ICH is used to connect and control peripheral devices. As CPU speeds increased data transmission between the CPU and support chipset, the support chipset eventually emerged as a bottleneck between the processor and the motherboard. Accordingly, starting with the Intel 5 Series, a new architecture was used that incorporated some functions of the traditional north and south bridge chips onto the CPU itself, with the remaining functions being consolidated into a single Platform Controller Hub (PCH). This replaces the traditional two chip setup. ICH The first version of the ICH was released in June 1999 along with the Intel 810 northbridge. While its predecessor, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
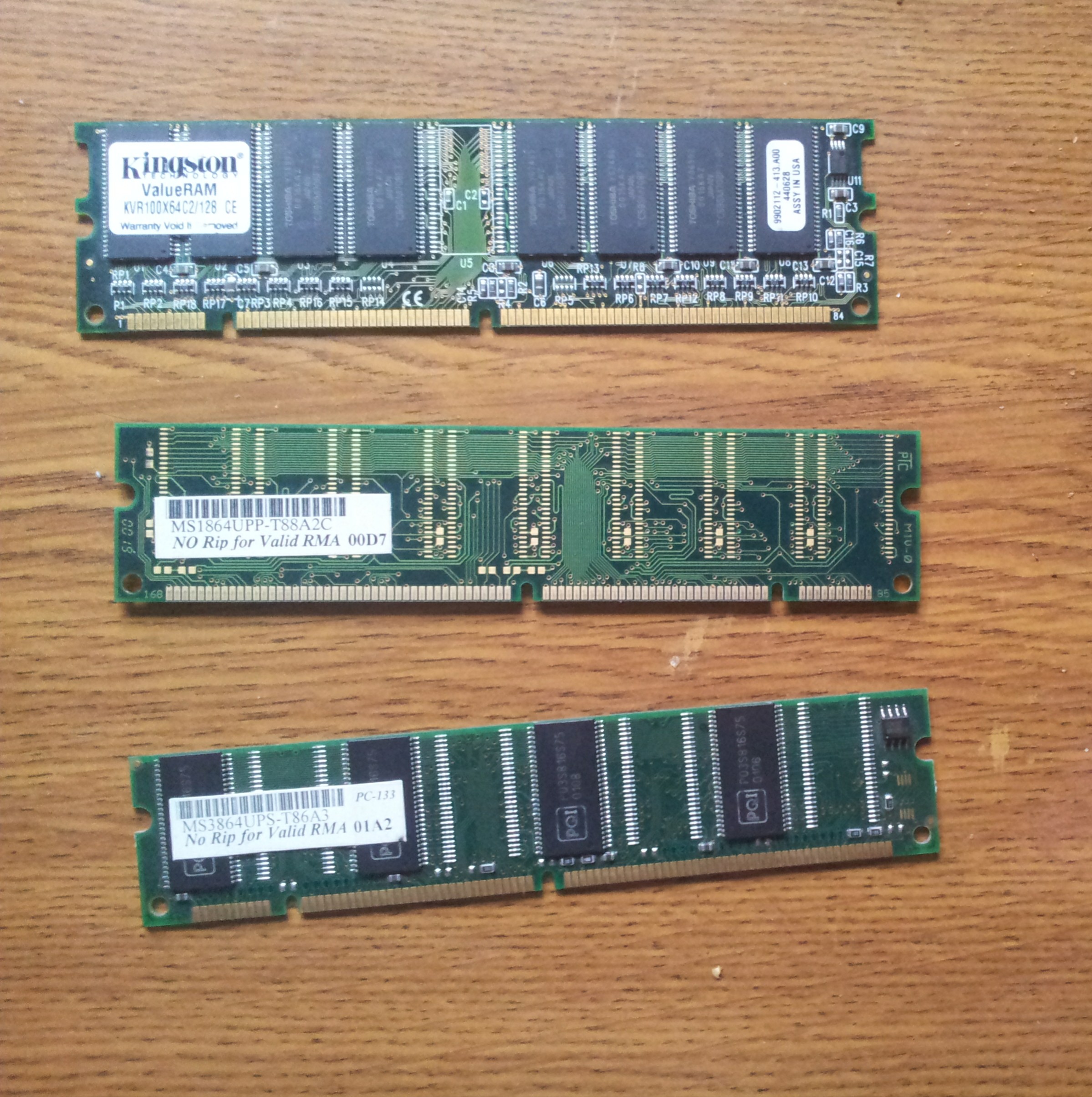
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules will not work in DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa. Compared to single data rate ( SDR) SDRAM, the DDR SDRAM interface makes higher transfer rates possible by more strict control of the timing of the electrical data and clock signals. Implementations often have to use schemes such as phase-locked loops and self-calibration to reach the required timing accuracy. The interface uses double pumping (transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal) to double data bus bandwidth without a corresponding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 423
Socket 423 is a 423-pin CPU socket used by the first generation of Pentium 4 processors, based on the Willamette core. It was replaced by Socket 478 in 2001. Technical specifications This socket houses any processor designed in the Socket 423 package. The socket was short-lived, as it became apparent that its electrical design proved inadequate for raising clock speed beyond 2.0 GHz. Intel produced chips using this socket for less than a year, from November 2000 to August 2001. It was replaced by Socket 478 Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs. Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and th ..., which being microPGA was cheaper to make. The processors used with this socket also have a locked multiplier which means that they are not overclockable unless the front side bus frequency is increased. However raising t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 478
Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs. Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based processor socket which was on the market for only a short time. Socket 478 was phased out with the launch of LGA 775 in 2004. Technical specifications Socket 478 was used for all Northwood Pentium 4 and Celeron processors. It supported the first Prescott Pentium 4 processors and all Willamette Celerons, along with several of the Willamette-series Pentium 4s. Socket 478 also supported the newer Prescott-based Celeron D processors, and early Pentium 4 Extreme Edition processors with 2 MB of L3 CPU cache. Celeron D processors were also available for Socket 478 and were the last CPUs made for the socket. While the Intel mobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDRAM
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generation of Rambus DRAM, DRDRAM was replaced by XDR DRAM. Rambus DRAM was developed for high-bandwidth applications and was positioned by Rambus as replacement for various types of contemporary memories, such as SDRAM. DRDRAM was initially expected to become the standard in PC memory, especially after Intel agreed to license the Rambus technology for use with its future chipsets. Further, DRDRAM was expected to become a standard for graphics memory. However, RDRAM got embroiled in a standards war with an alternative technology—DDR SDRAM—and quickly lost out on grounds of price and, later, performance. By around 2003, DRDRAM was no longer supported in new personal computers. PC main memory The first PC motherboards with suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Random Access Memory
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) technology. While most DRAM memory cell designs use a capacitor and transistor, some only use two transistors. In the designs where a capacitor is used, the capacitor can either be charged or discharged; these two states are taken to represent the two values of a bit, conventionally called 0 and 1. The electric charge on the capacitors gradually leaks away; without intervention the data on the capacitor would soon be lost. To prevent this, DRAM requires an external ''memory refresh'' circuit which periodically rewrites the data in the capacitors, restoring them to their original charge. This refresh process is the defining characteristic of dynamic random-access memory, in contrast to static random-access memory (SRA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Chipsets
This article provides a list of motherboard chipsets made by Intel, divided into three main categories: those that use the PCI bus for interconnection (the 4xx series), those that connect using specialized "hub links" (the 8xx series), and those that connect using PCI Express (the 9xx series). The chipsets are listed in chronological order. Pre-chipset situation An earlier chipset support for Intel 8085 microprocessor can be found at MCS-85 family section. Early IBM XT-compatible mainboards did not have a chipset yet, but relied instead on a collection of discrete TTL chips by Intel: * the 8284 clock generator * the 8288 bus controller * the 8254 Programmable Interval Timer * the 8255 parallel I/O interface * the 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller * the 8237 DMA controller Early chipsets To integrate the functions needed on a mainboard into a smaller amount of ICs, Intel licensed the ZyMOS POACH chipset for its Intel 80286 and Intel 80386SX processors (the 822 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)




